WIND POWER
Wind Power: history
Wind power is a renewable resource that is a consequence of the action of the sun on the Earth. In fact, the intensity of solar radiation differs across the globe and some areas can receive different amounts of sunlight.
An irregular heating of the earth's atmosphere, in addition to irregularities on the earth's surface and the rotation of the earth, creates wind.
The recent history of wind power has a similar impetus to that of alternative fuel sources in general: it was an idea born from the 1970's Oil Crisis. It does, however, have a more extensive history reaching back into to late 19th century in the colonization of the American West; millions of windmills were erected for irrigation and cattle purposes to facilitate the growing number of farms and ranches, but soon fell into disrepair as inexpensive energy sources became more widespread and grid power extended its reach into rural areas which used small electric wind systems. Outside of the US, however, wind power has a broader history. In fact, there was evidence that boats were propelled along the Nile as early as 5000 BC via wind energy. China used wind for pumping water several thousands of years ago.
Wind Power: harnessing wind energy for power purposes
Wind is harnessed to make mechanical power or electricity. The kinetic energy from the wind is converted through various different processes to create mechanical energy. Although there exists some variety of the turbines, they all perform the same function as illustrated in the following drawing:
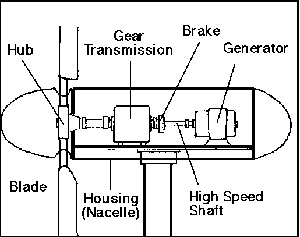 |
|---|
- Wind turbines, similar to propeller blades, are erected in areas of high wind flow.
- The movement of the turbine powers an electric generator. The power is fed through a transmission before being released into the generator. The transmission keeps the generator operating efficiently during different ranges of wind speed. This allows energy generation at all times, even when winds are slight. The result of this process is an electrical current.
- This energy is either stored for later use or used directly.
There are two types of modern turbines – with horizontal and vertical axis – both of which work similar to one another and as described above. Between the two types, they come in an array of sizes from small 100 watt units for single homes to much larger ones (with a blade diameter greater than 50 m). These larger turbines can generate 1 MW of electricity.
|
|---|
General Advantages of Wind Power
The advantages of Wind power are many, including practical, environmental as well as economic ones.
Worldwide, the total kinetic energy contained in wind is more than 80 times that of human energy consumption. While only a fraction of this can be used for electricity purposes, the potential-given by future technological developments-is great.
• renewable source of energy;
• clean, non-polluting source of energy;
• curb the demand and use of fossil fuels;
• emit no air pollution of greenhouse gasses.
In California wind plants have offset the emission of more than 2.5 billion pounds of carbon dioxide, and 15 million pounds of other pollutants.
• wind energy is free!
• the cost of installation and maintenance has dramatically decreased in recent years;
• future technology ensures only a continual decrease in the prices;
• no fuel to purchase and low operating costs.
As a result, the lifetime investment is much lower than with most fossil-fuel systems.
General Disadvantages
One of the primary disadvantages to wind power is the natural variability of wind in any given area. Indeed there are certain areas with extremely high average wind speeds, but in most places, wind exposure is quite variable. Wind energy can only be stored with a battery, otherwise it is not available. In the latter case, not all energy demands can be met through the natural timing of winds. For these reasons, it may not be a viable option for some areas. One other disadvantage is the competition for other -more highly valued and profit generating-land uses.
• the initial investment is often higher than with fossil fuel systems;
• the higher costs is mostly due to the machinery which is involves;
• other costs include site preparation and installation.
• noise pollution via the rotor blades;
• aesthetic impacts ("visual pollution");
• bird deaths.
It is important to keep in mind that many of these problems have been resolved with increasing technology. Avian mortality, however, is still being studied.
|

