SOLAR PANELS
Solar power is one of the first things that come to most people's minds when the subject of alternative energy comes up. Solar power first gained wide public awareness during the 1970's energy crisis, and while it may not be such a hot topic these days, solar technology has made great advances since then.
We use solar power in two different types of panels:
• Solar Thermal Panels
• Solar Electric Panels
Solar Thermal Panels
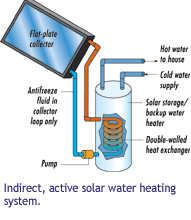 The first widespread residential use of solar energy came in the form of solar thermal heating panels. Solar water heaters are generally classified as "direct" or "indirect", depending on the types of fluids they circulate, and as "active" or "passive", depending on how they circulate those fluids:
The first widespread residential use of solar energy came in the form of solar thermal heating panels. Solar water heaters are generally classified as "direct" or "indirect", depending on the types of fluids they circulate, and as "active" or "passive", depending on how they circulate those fluids:
• Systems that heat pressurized water in the collector are referred to as "open-loop" or "direct" systems. Those that place a heat exchanger (for freeze protection) between the collector and the pressurized, potable water are referred to as "closed loop" or "indirect" systems. Indirect systems are used in cold climates.
•
"Passive" solar water heating systems use natural convection or municipal waterline pressure to circulate the fluid through the collector to the storage tank. They have no pumps or controllers and are less expensive, more reliable and easier to maintain than active systems. Passive systems are used only in mild climates where the potable water pipes running to the system will not freeze. Batch heaters (also known as "bread box" or integral collector storage systems) and thermo siphon systems are the most common types of passive systems for buildings.
"Active" systems use a pump to circulate the fluid through the system (many systems are now sold with a small solar electric collector to power the pump). Active systems are usually more expensive than passive systems, but they are also more efficient. They must be used in cold climates where hard freezing occurs. Flat-plate collector systems are the most common type of active system for buildings (although systems that use evacuated-tube collectors are also available).
The amount of hot water your system produces and the efficiency with which that water is produced depends, in part, on the amount of solar energy at your site, the type and size of your system, and proper installation. In almost all climates, you will need a conventional backup system to supply water when there is not enough solar-heated water to meet the demand. In fact, many building codes require you to have a conventional water heater as a backup.
Solar Electric Panels
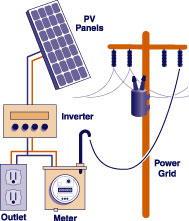 Photovoltaic (PV) panels, which use sunlight to produce electricity, are much more efficient for their purpose than their solar thermal cousins. They are also much more useful in northern climates. While the manufacturing process and the mechanism by which they work are more technical than solar thermal panels, they are much simpler to install and maintain in actual use. What follows is an overview of the function and purpose of photovoltaic panels, as well as the many benefits they have in alternative energy systems.
Photovoltaic (PV) panels, which use sunlight to produce electricity, are much more efficient for their purpose than their solar thermal cousins. They are also much more useful in northern climates. While the manufacturing process and the mechanism by which they work are more technical than solar thermal panels, they are much simpler to install and maintain in actual use. What follows is an overview of the function and purpose of photovoltaic panels, as well as the many benefits they have in alternative energy systems.
Solar electric panels are probably one of the simplest alternative energy sources to use. They can be mounted on a rooftop or a freestanding solar array rack.
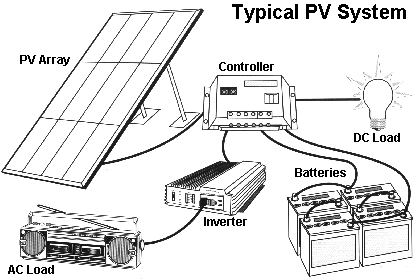 Once mounted, a wire needs to be run from the solar panel to a solar charge controller, and a wire needs to be run from the charge controller to a deep cycle battery bank. If the building's electrical system runs on DC power, the battery bank can be wired directly into the system.
Once mounted, a wire needs to be run from the solar panel to a solar charge controller, and a wire needs to be run from the charge controller to a deep cycle battery bank. If the building's electrical system runs on DC power, the battery bank can be wired directly into the system.
Multiple solar panels increase the wiring complexity a bit, and of course, most homes will use 120 volt AC power or a combination of AC and DC power. AC power systems will require the use of an inverter to convert the DC battery power into useable 120 VA power.
However, the fundamentals of using solar power remain simple. The solar panels turn sunlight into electricity, and that power is stored up in a battery bank for household use. The household power needs are drawn out of the stored battery power, and the solar panels recharge the batteries when their charge drops below a certain level.