The angle which the Sun’s rays form with the normal, or line perpendicular to a surface, is called angle of incidence. The amount of energy which a surface absorbs (and consequently the intensity of the current produced by a photovoltaic panel) depends on this angle: e.g. in the summer months, the energy intercepted by the earth is higher because the inclination of the rays is closer to the normal. If the aim is to obtain electric energy (but it is obviously the same for heat, too) through the absorption of solar energy by a fixed, flat absorbing surface, it is necessary to position and incline it with respect to the direction of incident radiation so as to maximize absorption.
In this experiment, we aim to determine the most favourable angle of incidence of the solar panel and, in general, the relationship between the angle of incidence and the power output of a photovoltaic panel.
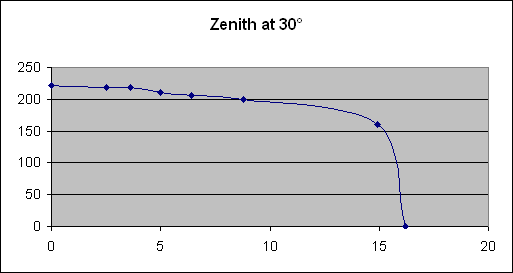
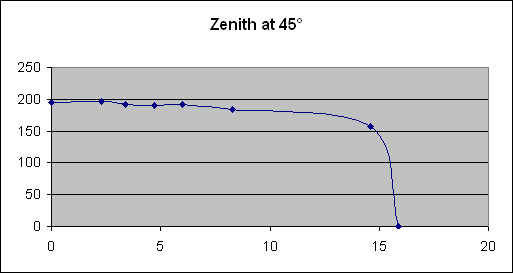
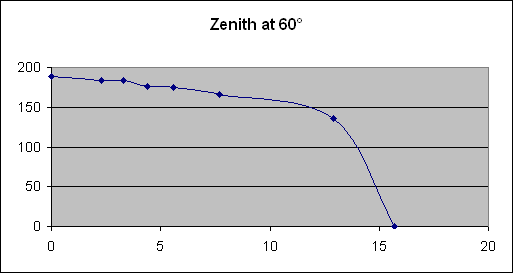
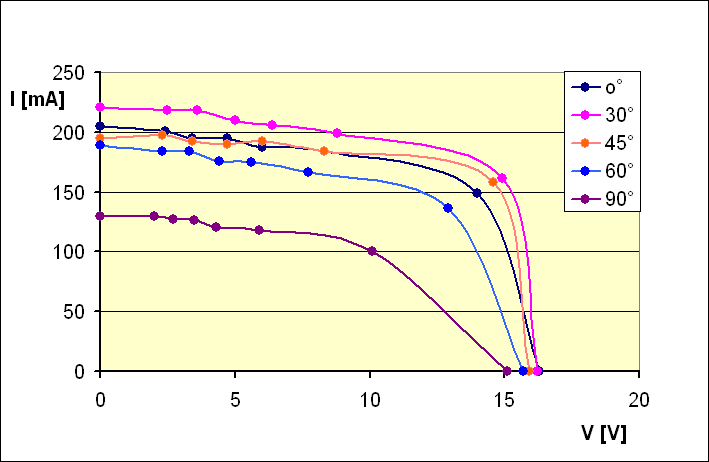
In order to carry out this study, we employed a system which allowed us to plot the curve of the properties of a photovoltaic panel by establishing a link between voltage and current. We noticed the different properties, each of them with a different angle of incidence between the panel and an artificial light source. At the end of our study, we noticed that the highest output of the panel results when the Sun’s rays are perpendicular to the surface of the panel.
The results of this study show that the maximum power output of a photovoltaic panel results when the Sun’s rays are perpendicular to the surface of the panel as long as possible.
DATA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GRAPHS |
|---|
 |
 |
 |
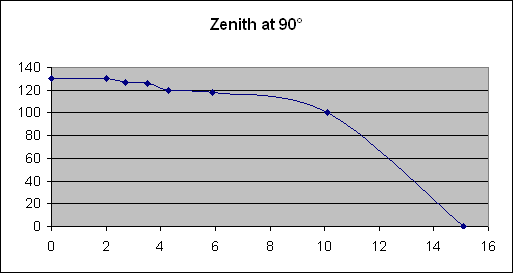 |
| PROPERTIES AT DIFFERENT ZENITH ANGLES |
|---|
 |